About assistive technology
Together transforming lives through assistive technology.
©UNICEF Rwanda
What is assistive technology?
Assistive technology (AT) is an umbrella term for assistive products such as wheelchairs, hearing aids, prostheses, eyeglasses or digital devices, and their related systems and services.
The scope of assistive technology is large, and to focus the work, ATscale identified five priority products for its initial phases, namely wheelchairs, prostheses, hearing aids, eyeglasses and digital assistive technology (including smartphones).
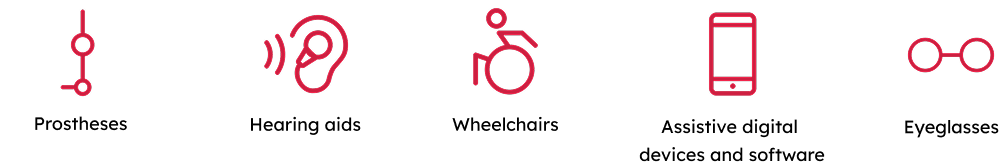
We selected these through an analysis and assessment of the 50 products on the WHO Priority Assistive Product List, which considered the level of unmet need and the potential for impact through market shaping. This focus does not exclude other assistive products, however, especially in support of country programmes.
The scale of the challenge
Despite its transformative potential, one billion people worldwide lack access to the assistive technology they need.

Today, more than 2.5 billion people around the world require one or more assistive products. By 2050, this number is expected to grow to 3.5 billion.
Those who can benefit from assistive technology include persons with disabilities, older people and people with mental and physical health conditions, including acute or chronic disease, disorder, injury or trauma.
Assistive technology helps people throughout their lives: for children with support for learning; for adults to be able to work productively; and for older people as they seek to maintain independence.
However, access varies hugely, from 90 per cent in high-income countries to 10 per cent in low-income countries. This inequity exacerbates other inequalities, such as restricted opportunities for education and employment, and diminished quality of life.
Without action, the assistive technology divide will deepen inequalities and leave the most marginalised even further behind.
Watch this video about how assistive technology changes lives
The first ever Global Report on assistive technoloy was launched in May 2022. The landmark report by WHO and UNICEF, sponsored by ATscale and AT2030, presents shocking data on the global need for assistive technology and lack of access to it.
The report outlines how a comprehensive understanding of access to assistive technology is needed to strengthen national systems and advance the global assistive technology sector; and how global, transnational and national strategies are needed to unify and raise the priority level of the assistive technology sector itself.
Why assistive technology matters
It’s life-changing: access to assistive technology can enable people to live healthier, more productive, more independent, and more dignified lives, and to participate in education, the labour market and their communities. It facilitates access to and participation in education; is vital for livelihoods and employment; can support independence and chronic condition management, especially for ageing populations, and can be crucial to survival in humanitarian settings.
It makes economic sense: the benefits of assistive technology extend beyond the individual user to wider society, by boosting economic productivity, reducing healthcare costs by enabling preventive care and independent living, and promoting inclusivity and equality. For every dollar invested, there is an estimated nine-dollar return. Early access to assistive technology can improve a child´s lifetime earnings by up to US$100,000.
It supports global development: assistive technology is recognized as a critical enabler across the range of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) relating to education, health, economic empowerment and other issues. Overall, it allows people to overcome barriers that would otherwise limit their potential and therefore supports efforts to ‘leave no one behind’.
What is standing in the way?

| |
System-level barriers | |
| |
| |
Market-level barriers | |
|
How we catalyse change
ATscale, the Global Partnership for Assistive Technology, brings together governments, donors, multilaterals, the private sector, users of assistive technology and organizations of persons with disabilities to deliver systemic, sustainable change.
- We support countries in building inclusive policies, systems and workforces.
- We shape markets to improve availability and affordability of essential products.
- We generate global momentum through advocacy and evidence.
- We work in partnership to increase innovation and impact.



